In C, primitive types are just numbers.
printf("%d, %u, %f, %x", '\0\0\0A', -35, 0.5, "string");
// 65, 4294967261, 0.500000, ce1c2008
Some are signed, unsigned, floating point, or pointers. But all of them are numbers of a certain width. Floats and pointers support a subset of the operations integers do, but all primitive types in C support some level of arithmetic.
printf("%d, %x, %ld", true * 6, argv[0]+3, 0.6);
// 6, 4303b661, 99179430350296
Compound types are either a collection of terms of different types (struct),
of the same type (arrays), or a list of aliases to a singular place in memory (union).
struct response {
char abbr[3];
enum {SUCC, ERR} tag;
union {
int succ;
char err[4];
};
};
Unions are usually annotated with a tag of which alias is in use. Doing this in C requires explicit thought and attention, even though this behavior is needed in most contexts.
In this spirit, enumerations are interchangeable with integers.
enum {A, B, C} x = 630;
enum {D, E, F} y = A;
y == D; // True
All of this allows for transparent memory management. The price paid is that it’s a lot harder to cleanly represent data with C. The programmer has to be constantly paranoid about invalid states whenever handling data.
Instead of modeling data based purely on its representation in memory. We can model data types more abstractly and mathematically.
Algebraic Description of Types (ADT)
Using ADT, a type is just a set of terms. Values outside of these terms are unconstructable.
enum Boolean {
True,
False,
}
The mathematical notation for type theory often works with the number of terms in the type. For example, the boolean type is commonly
called 2 in mathematical contexts.
We can combine types into larger types using product and sum types.
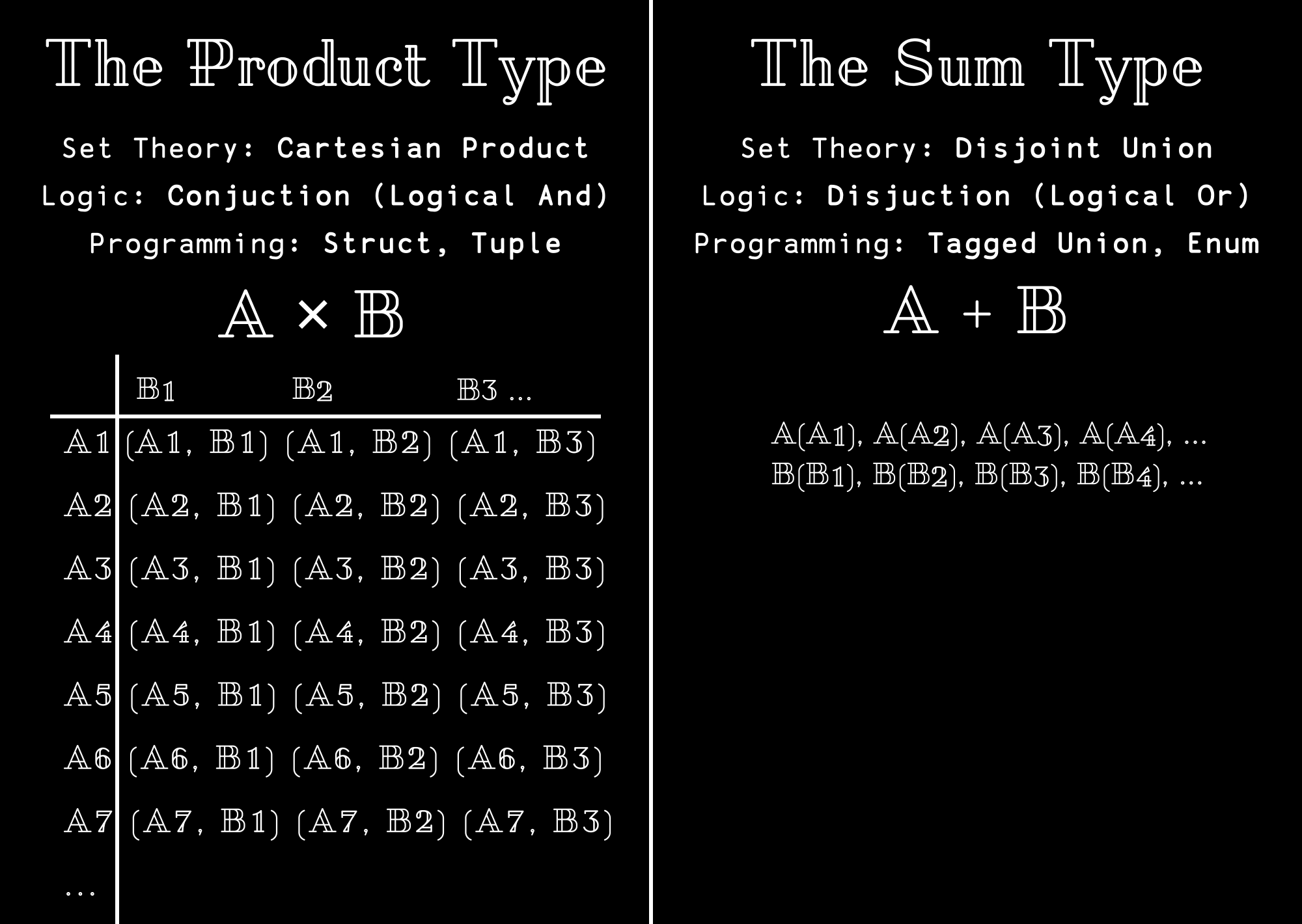
A product type combines types in a similar fashion as a struct in C.
struct Person {
Name(String),
Age(u32),
}
The number of terms in a product type is equal to the product of the number of terms in the two combining types.
A sum type is analogous to a tagged union, representing either one value or another.
enum Response {
Succ(u32),
Error,
}
The number of terms in a sum type is equal to the sum of the terms in the combining types.
Types that represent functions with one argument are also possible, reducing down to the exponentiation.
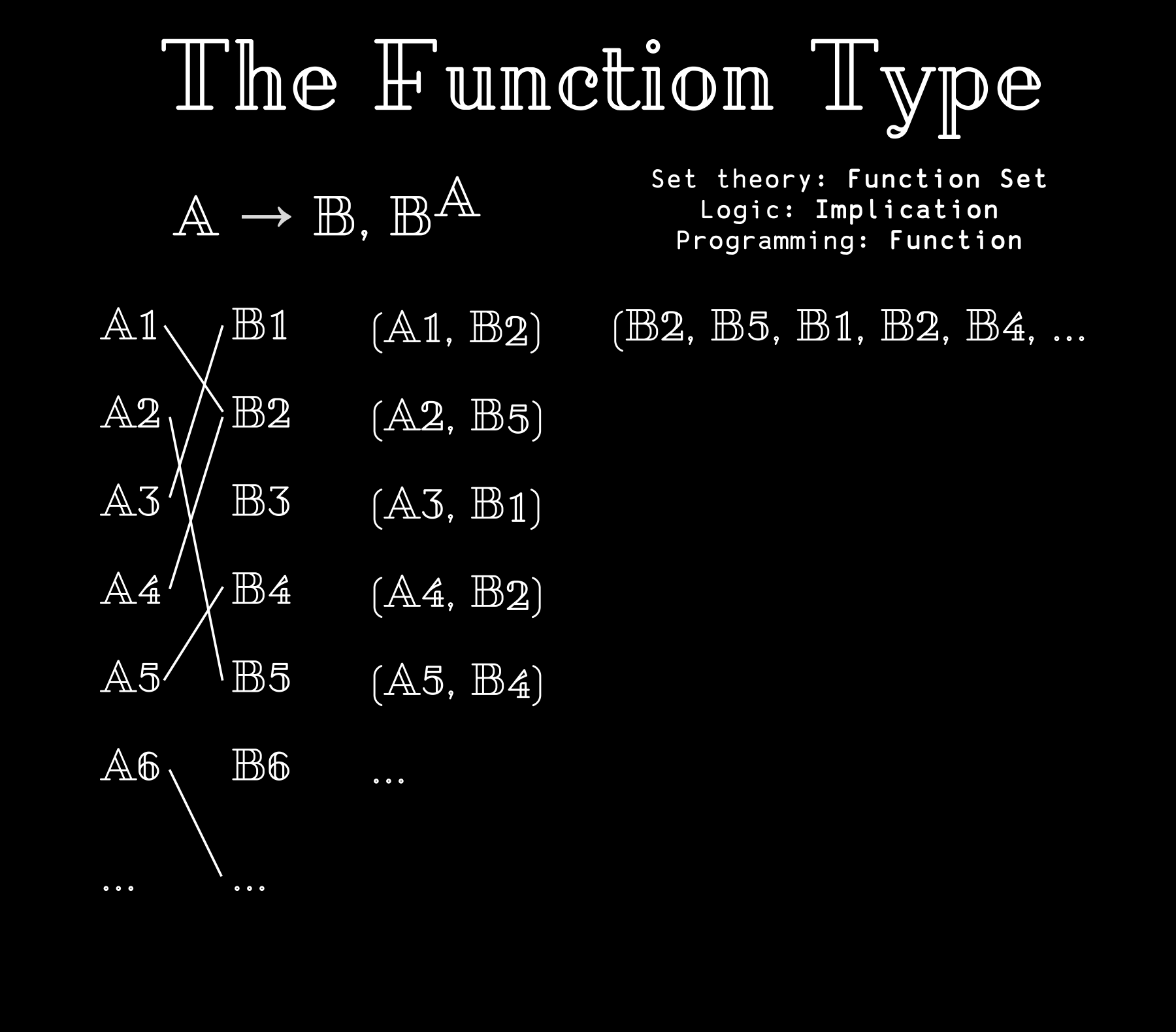
A function with multiple arguments is possible via currying, returning a function with one less argument.
> x = (+ 2)
> x 3
5
Now, Prove that numbers exist.
No, seriously. Do it. Or less ambiguously, name a valid number.
5, TREE(3), perhaps 3,735,928,559? Congratulations, you have proved that numbers exist!
Now, prove that the type returned by rusts exit function exists. Or less ambiguously, name a valid term the exit function returns.
…
No answer? That is because the type exit returns (in rust) has no valid term. And therefore this function cannot return since it isn’t capable of returning a valid value.
The obvious consequence of this is that the noreturn “type” in C can be replaced by a null type. But this has a deeper implication of being able
to express statements in a type and prove they are true if the type is inhabited.
Similarly, proving that Result<A,B> exists proves that A or B exists (aka. A + B != 0). And (A, B) proves that A and B exists (aka. A * B != 0)